Headaches – Migraine

Migraine Headaches
- A painful throbbing headache
- Heightened sensory awareness
- Light sensitivity
- Sound sensitivity
- Sensitivity to smells
- Nausea or vomiting
- Cognitive difficulty
- Loss of appetite
- Nasal/sinus congestion
- Visual disturbance
- Numbness
- Tingling
BOTOX® is a preventive treatment. It prevents headaches and migraine attacks in adults with Chronic Migraine before they even start. BOTOX® is injected using small needles. The injections are done in shallow muscles, just beneath the skin. The shots take about 10 minutes, every 3 months, and are done right in your doctor’s office.BOTOX® prevents, on average, 8 to 9 headache days and migraine or probable migraine days a month.
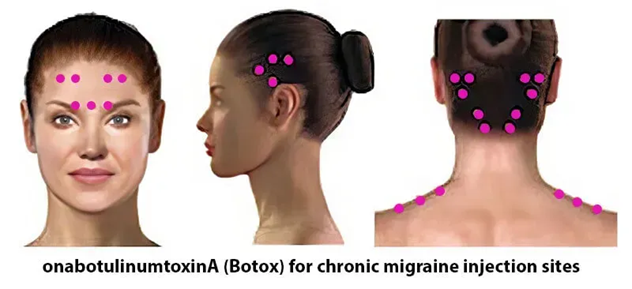
- What are the common symptoms of Chronic Migraine?
- Moderate to severe headaches or head pain
- Head pain that causes throbbing, pounding, or pulsating sensations
- Nausea and/or vomiting
- Sensitivity to light, noise, and/or smells
- Attacks that last from 4 hours to several days
- If you are experiencing this 15 times or more a month with each headache lasting 4 hours or more, you may have Chronic Migraine.
What is the treatment for acute migraines?
- OTC pain relievers
- Prescription pain and anti-nausea medications
- New class of medications with minimal side effects
- Applying cold compress to the head
- Resting in a quiet, dark room
- Injection pain medication is given at the site if all of the above fails. Results are noticeable within 30 minutes.
What is the treatment for chronic migraines?
There are number of new medications in the market for prophylaxis of chronic migraine headaches. These newer medications work faster and have fewer side effects. They help reduce both the frequency and the intensity of your migraine headaches. You will need to take medications for acute migraine episodes less frequently. Give us a call today and book a consultation, we can discuss your symptoms and finally find relief.
Eligibility Criteria
- 15 headache days per month, lasting 4 hours or
- Few headaches days that last all day long
- Do not respond to prescription medications
- Failed 2 preventative medications
Statistics
- Number of adults with chronic migraines:3.2 Million
- Treatments take 15 minutes:1 in 10
- Lasts 3-6 months depending on the type of toxin used80.1%
This Treatment…
- Is FDA approved for prevention of Migraines
- Treatments take 15 minutes
- Lasts 3-6 months depending on the type of toxin used
Tension Headaches
A tension headache is the most common type of headache. It is pain or band like pressure around the head. Tension headaches occur when neck and scalp muscles become tense. Any activity that causes the head to be held in one position for a long time without moving can cause a headache.

Other triggers include
- Physical or emotional stress
- Fatigue or overexertion
- Sinus infection
- Jaw clenching or teeth grinding
- Alcohol use
- Excessive smoking
What are the options?
Some people with tension headaches have very sensitive areas, known as trigger points, at the back of the neck area. Injecting a local anesthetic into these areas may eliminate the pain and prevent the headache from recurring. There are also number of medications that can help keep tension headaches at bay. If OTC medications aren’t giving you the relief you need, talk to us about the treatment options that might be right for you.
